케라스와 함께하는 쉬운 딥러닝 (16) - 순환형 신경망(RNN) 기초
25 Jun 2019 | Python Keras Deep Learning 케라스순환형 신경망 2 - RNN 구조 기초
Objective: RNN의 기본적인 구조를 이해하고 케라스로 이를 구현해본다
지난 포스팅에서 RNN의 특징을 CNN이나 MLP와 같은 feedforward net과의 차이를 중심으로 알아보고, 가장 기본적인 RNN 셀(SimpleRNN)을 케라스로 구현하는 방법을 알아 보았다. 이번 포스팅에서는 비슷하지만 조금 더 우수한 성능을 내는 RNN 셀 구조인 LSTM에 대해 알아보자.
LSTM
LSTM은 Long Short-term Memory의 약자로, 기본적인 RNN 셀과 달리 hidden state 뿐 아니라 cell state도 다음 단계로 전이된다. LSTM의 이러한 복잡한 구조는 긴 sequence에서 정보가 유실되는 long-term dependency 문제를 어느 정도 완화해 준다. LSTM에 대한 자세한 설명은 이 포스팅을 참고한다.
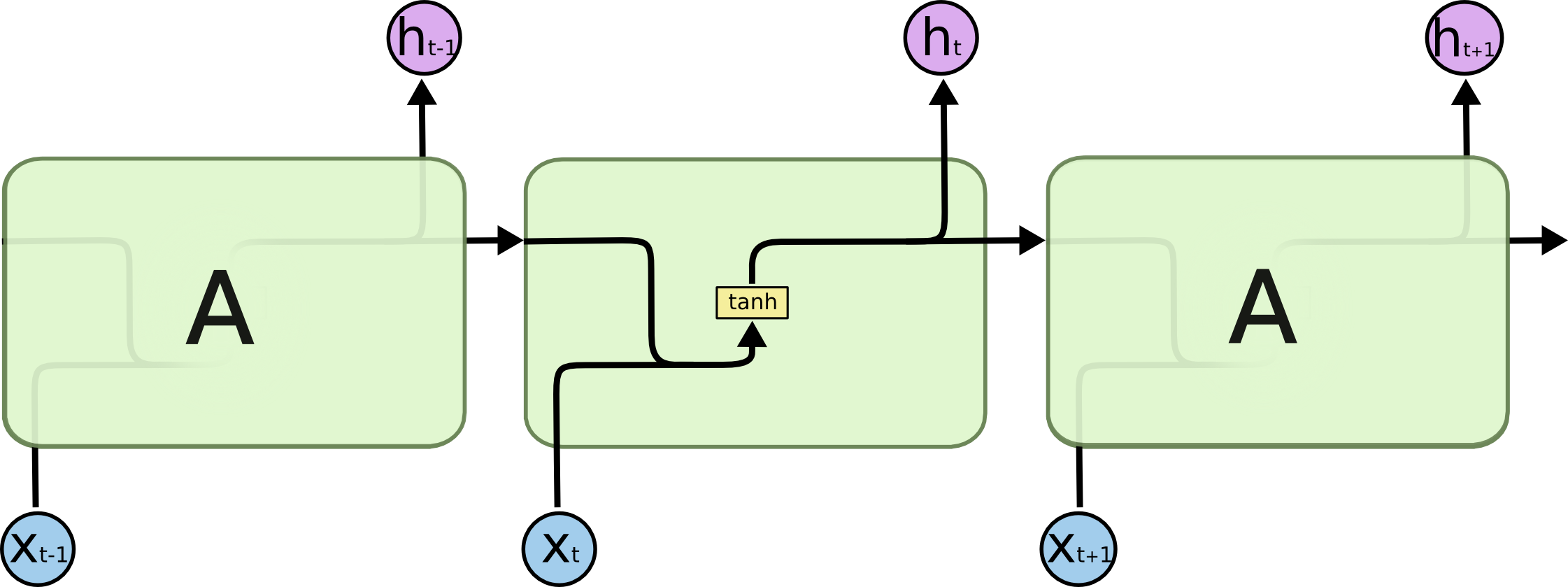
- 기본적인 RNN 구조
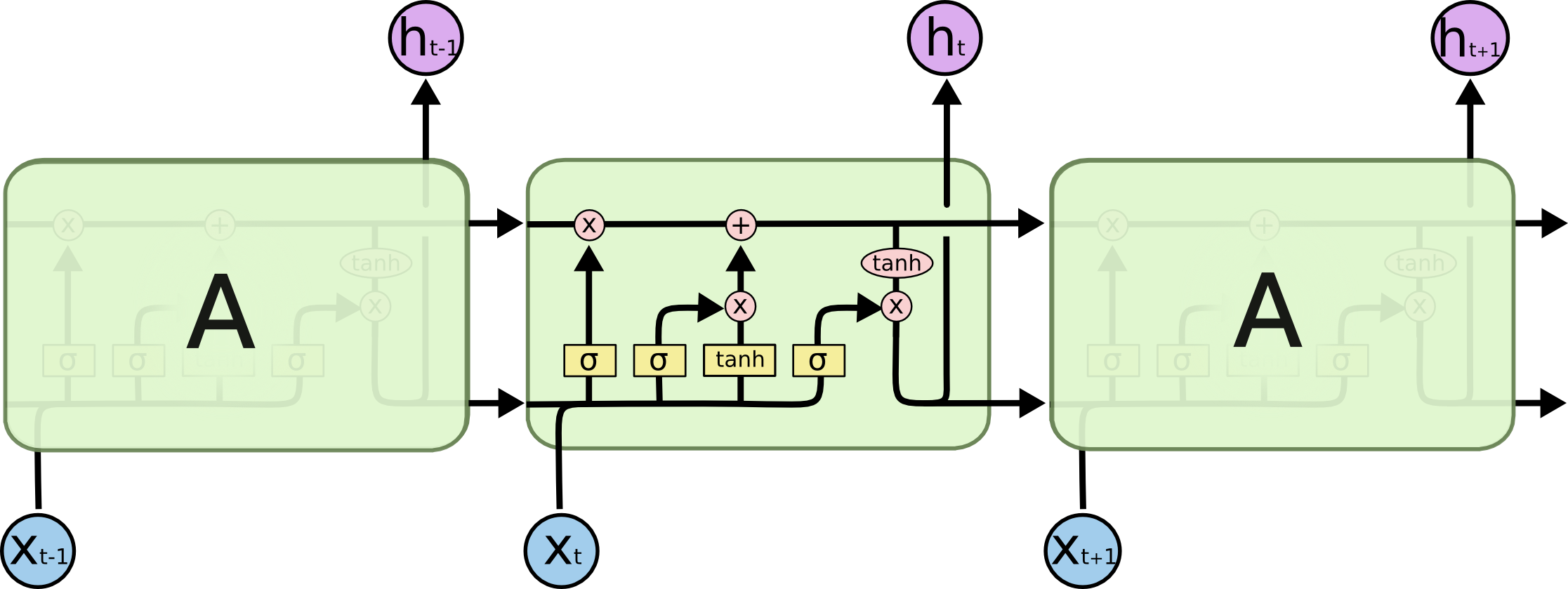
- LSTM 구조
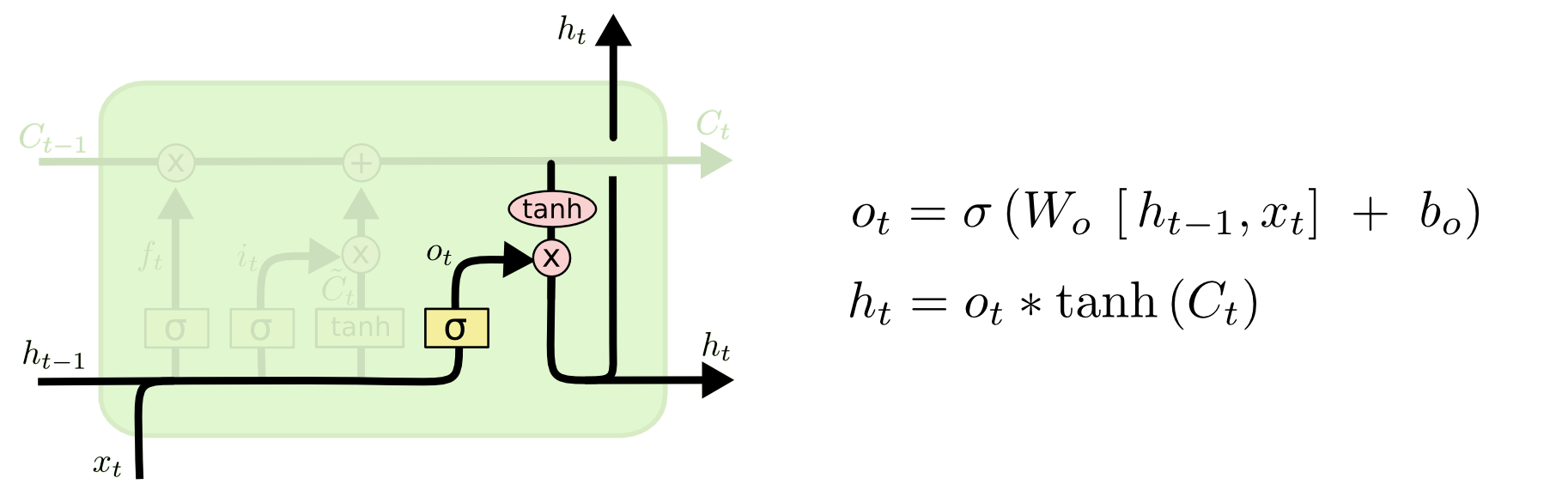
- Hidden State (h_t)
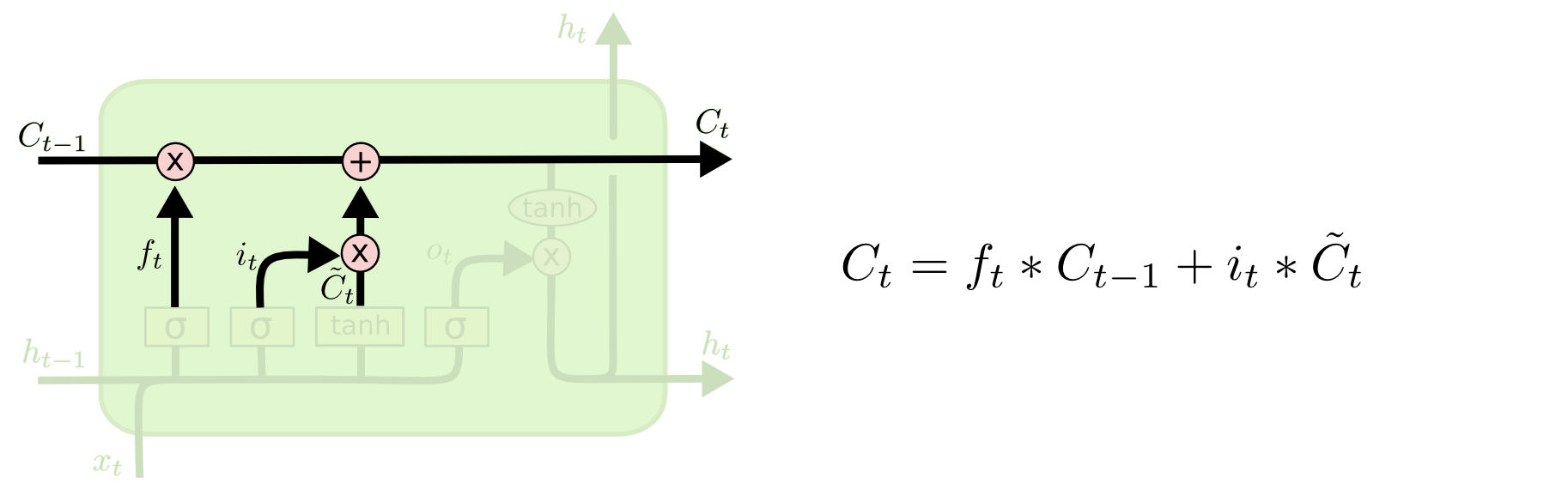
- Cell State (C_t)
케라스에서 LSTM 구현하기
# 셀 사이즈 50의 lstm 셀 생성
lstm = LSTM(50)(Input(shape = (10, 30)))
print(lstm.shape)
(?, 50)
SimpleRNN과는 달리 LSTM은 2개가 아닌 3 가지의 state가 리턴된다(순서대로 output, hidden state, cell state). 동일하게 return_sequences 파라미터를 False로 설정하면 스칼라 값이 반환된다.
lstm = LSTM(50, return_sequences = False, return_state = True)(Input(shape = (10, 30)))
print(lstm[0].shape) # shape of output
print(lstm[1].shape) # shape of hidden state
print(lstm[2].shape) # shape of cell state
(?, 50)
(?, 50)
(?, 50)
return_sequences 파라미터를 True로 설정하는 경우.
lstm = LSTM(50, return_sequences = True, return_state = True)(Input(shape = (10, 30)))
print(lstm[0].shape) # shape of output
print(lstm[1].shape) # shape of hidden state
print(lstm[2].shape) # shape of cell state
(?, ?, 50)
(?, 50)
(?, 50)
아래와 같이 output, hidden state, cell state를 서로 다른 변수로 받을 수도 있다.
output, hidden_state, cell_state = LSTM(50, return_sequences = True, return_state = True)(Input(shape = (10, 30)))
print(output.shape)
print(hidden_state.shape)
print(cell_state.shape)
이번 포스팅에서는 기본적인 RNN 셀과는 조금 다른 구조를 갖는 LSTM에 대해서 알아보았다. 다음 포스팅에서는 또 다른 형태의 RNN 구조에 대해서 알아보자.
전체 코드
본 실습의 전체 코드는 여기에서 열람하실 수 있습니다!
